Why You Should Add Wi-Fi to Your Portfolio Offering
The typical IT infrastructure and unified communications deployment are always evolving to fit the current needs of the modern office. IP PBXs, IP phones, facility access devices, security cameras, switches, and other devices all facilitate the transfer of information for the users within a business. As workplaces embrace hybrid workspaces, mobile workstations, and greater reliance on Wi-Fi-compatible devices, Wi-Fi access points have become a staple for the typical IT deployment. Within this guide, we’ll discuss the major advantages that Wi-Fi brings to your client's businesses and the features that you can leverage with Grandstream’s wireless portfolio to create a competitive wireless offering.
Wi-Fi is no longer a “nice-to-have” investment within businesses, schools, hotels, and other organizations. It is a critical system that workers need to stay productive throughout the day and that customers expect at shops and hotels. Wi-Fi brings a variety of benefits and advantages to businesses, such as increased collaboration and productivity, simple and flexible infrastructure, and increased customer satisfaction in environments where public Wi-Fi is necessary.
Download a PDF copy of the Guide
 Increased Productivity and Collaboration
Increased Productivity and Collaboration
The ability for a worker to freely move among their business to meet with colleagues, collaborate on projects, and conduct their responsibilities is absolutely necessary within a modern business. As hybrid workspaces continue to be adopted, and part-time remote work is here to stay in the post-pandemic era, Wi-Fi is a needed technology for workers to operate. Laptops break the tether between productivity and the desktop and allow users to move more freely between work stations within their physical space. A series of Wi-Fi access points enables this movement around a workspace while maintaining a fast internet connection.
Modern Wi-Fi access points offer speeds at or well above one Gigabit, which provides a rapid connection even when multiple simultaneous devices are running high-bandwidth applications such as video and audio conferencing. This helps maintain a high level of productivity no matter a user’s location within a wireless environment. Modern devices also offer QoS (Quality of Service) standards and MU-MIMO (Multiple-user, multiple-input, multiple-output technology) which allows a Wi-Fi AP to better communicate with multiple devices at the same time. Both these Wi-Fi features come together to provide your customer’s business with a rapid internet connection that can dynamically adjust bandwidth requirements based on the client device’s requirements.
Simple and Flexible IT Infrastructure
A Wi-Fi portfolio enables installers to create simple and flexible IT infrastructures for their clients while maintaining the fast connection speeds required for business productivity. Users have the ability to stay mobile and the network requires less of an upfront investment, is easier to manage post-deployment, and can easily be scaled up should the business needs grow or change. This is achieved through less ethernet cabling running throughout the entirety of a facility, a variety of access points supporting different bandwidth requirements, and easy scalability through cloud-based provisioning and management.
 In today’s business IT infrastructure, Wi-Fi compatibility comes with most devices. Laptops, IoT smart devices, facility speakers/paging devices, IP phones, and even video conferencing systems can run through a wireless connection. This means that less ethernet cabling is required throughout a deployment in order to provide an internet connection. This also makes Wi-Fi environments more flexible than a traditional ethernet installation. New wireless devices can be installed without constraints and without having to run complicated wires to their location.
In today’s business IT infrastructure, Wi-Fi compatibility comes with most devices. Laptops, IoT smart devices, facility speakers/paging devices, IP phones, and even video conferencing systems can run through a wireless connection. This means that less ethernet cabling is required throughout a deployment in order to provide an internet connection. This also makes Wi-Fi environments more flexible than a traditional ethernet installation. New wireless devices can be installed without constraints and without having to run complicated wires to their location.
Providing an internet connection to new parts of a building only requires one new cable path and a Wi-Fi access point at the end of it. On top of this, there are a variety of access points that can be selected depending on the needs of the business. Each provides varying levels of connection speed, range, and maximum client devices. Lastly, modern access points can be provisioned both on-site and through a cloud-based system, providing installers and IT teams with the ability to easily scale entire networks of APs at once.
Increased Customer Satisfaction
 If you go to an airport, hotel, or café, you’ll typically have access to a public Wi-Fi network. A wireless network is not only a necessary feature in offices, but also in areas where customers would need to access the internet for work, entertainment, or even make purchasing decisions. Modern access points come with various tools to customize each network to the needs of the particular business and its customers. Multiple SSIDs and SSID customization, captive portals, and bandwidth rules are three key features when it comes to creating a Wi-Fi environment that satisfies the customers of a business while not jeopardizing the operations of the business itself.
If you go to an airport, hotel, or café, you’ll typically have access to a public Wi-Fi network. A wireless network is not only a necessary feature in offices, but also in areas where customers would need to access the internet for work, entertainment, or even make purchasing decisions. Modern access points come with various tools to customize each network to the needs of the particular business and its customers. Multiple SSIDs and SSID customization, captive portals, and bandwidth rules are three key features when it comes to creating a Wi-Fi environment that satisfies the customers of a business while not jeopardizing the operations of the business itself.
Most access points can also designate a maximum amount of clients that can be connected to a particular network SSID at any one time. In networks that can experience large, periodic bounces in use, this can make the difference between a stable network and a broken one. In most cases, this will be used to prevent public network access from slowing down the total traffic through the access point.
Captive portals enable organizations to create an authentication barrier that must be crossed before a user can gain access to a public network. This authentication can be as simple as checking a terms and agreements option or having to authenticate the connection via social media or a landing page. This step can typically be highly customized depending on the business, even requiring name, email, and payment information from the user. This is particularly helpful when the organization wants to limit access to their free WiFi network, or engage with customers who used their network later on.
Sometimes, deployment will require you to limit bandwidth to ensure the performance of the network. Business-grade access points will allow organizations to throttle bandwidth through the access point based on SSID, MAC addresses, and even IP addresses. Typically, this can even be assigned to happen on a scheduled basis to only kick in during peak-usage periods to protect the user experience.
Grandstream's Wi-Fi Portfolio
Increased collaboration and productivity, simple and flexible infrastructure, and increased customer satisfaction are all key advantages that you can take advantage of when it comes to adding a networking solution to your portfolio. Wi-Fi provides some serious benefits that businesses can no longer go without, and that installers need to be able to deliver. Grandstream’s GWN series of Wi-Fi access points are designed with this in mind and enable installers to create customized Wi-Fi environments to deliver a perfect solution for their clients.
Our APs run the IEEE 802.11 Wi-Fi network standard. 802.11 is a set of media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) protocols for implementing a wireless local area network (WLAN). These protocols serve as the standard set of frequencies that all Wi-Fi devices connect over and include the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands. Grandstream’s APs support the latest iteration of 802.11, which is IEEE 802.11ac.
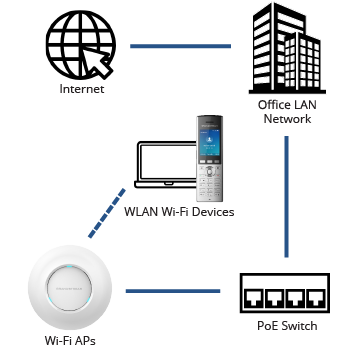 Grandstream’s series of access points support the following IEEE 802.11 standard data rates, depending on the access point:
Grandstream’s series of access points support the following IEEE 802.11 standard data rates, depending on the access point:
- 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6): 7.3 Mbps to 1201 Mbps
- 802.11ac: 6.5 Mbps to 867 Mbps
- 802.11a: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbps
- 802.11n: 6.5 Mbps to 300Mbps; 400Mbps with 256-QAM on 2.4GHz
- 802.11b: 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps
- 802.11g: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbps
All GWN APs except for the GWN7610 and GWN7602 support Wave 2 technology. Introduced in 2016, the Wave 2 supports higher bandwidth than the first generation of 802.11ac capable APs. Finally, our entire series supports beamforming technology and dual-band networks that offer 2.4G and 5G frequency bands. Beamforming technology allows APs to detect the locations of clients and focus their signals towards them, rather than in all directions. For our Wi-Fi 6 access point, OFDMA and improved MU-MIMO are two features that help create powerful wireless environments that can better handle high-volume requirements.
Competitive Advantages of the GWN Series
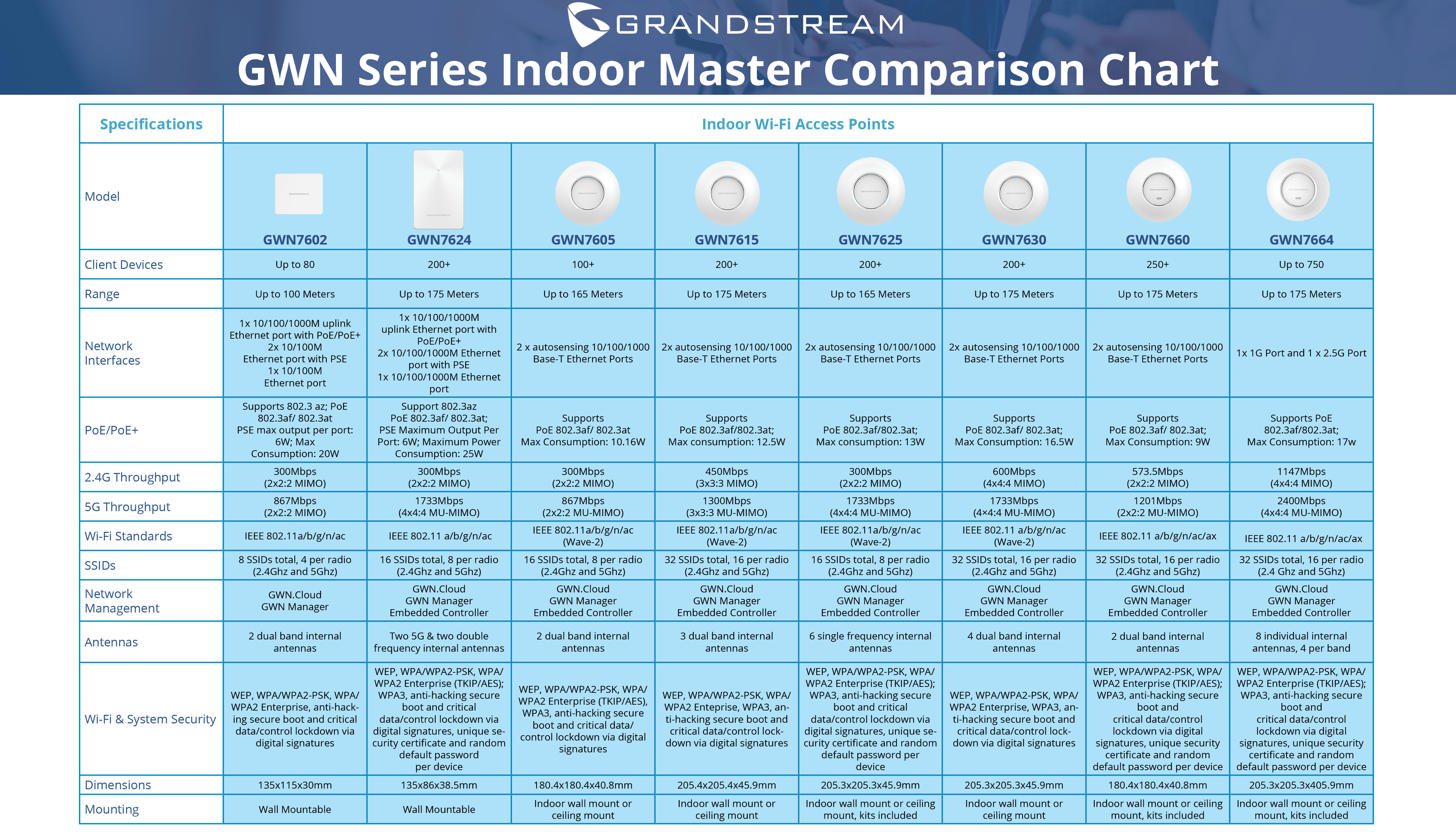
Grandstream’s Wi-Fi Access Points offer high-performance networking, tremendous Wi-Fi coverage range, fast and easy provisioning/management, outstanding network throughput, and support for a large number of clients per access point.
-
GWN.Cloud: Grandstream’s cloud-based Wi-Fi access point management platform. Configure, manage, and troubleshoot unlimited wireless deployments
- entirely from the cloud
- GWN Manager: For deployments with higher security standards, the GWN Manager is a premise-based version of the GWN.Cloud
- Built-in Controller: The GWN series can manage other GWN APs, check the device’s datasheet to learn more about this feature and the amount of APs that can be managed
- Beamforming Technology: Access points detect wireless clients and focus wireless signals towards them for better client performance
- Multiple Customized SSIDs: Up to 32 SSID channels depending on the access point, with customized client configurations, captive portal, and bandwidth limits
- QoS Standards: Prioritizes certain network traffic/devices so critical tasks don’t compete for bandwidth, can be customized based on deployment
- UL/DL OFDMA: Access points running on the 801.11ax standard perform better in dense environments and are designed to manage multiple Wi-Fi devices with varying bandwidth demands
- Blacklist: Prevents specific MAC addresses from connecting
- Connection Time: Enforce timeout of a connection and requires renewal
- Wireless Client Limit: Puts a cap on the maximum amount of wireless clients that can be connected to an SSID at a single time
- Bandwith Rules: A variety of rules that restrict the bandwidth usage of client devices
- Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) is a feature that is unique to Wi-Fi 6 that directly impacts uplink and downlink streams by more efficiently packaging different bandwidth needs across various client devices into "resource units". This allows Wi-Fi 6 access points to better handle deployments with a wide variety of deployment types (VoIP phones, laptops, IoT devices, etc)
- Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO) technology is another key feature of Wi-Fi 6. It was introduced with Wi-Fi 5 but further improved to increase the effectiveness of each spatial stream on the access point, which enables the AP to manage more simultaneous users with a slight decrease in client latency

























.webp?width=250&height=131&name=how-to-use-gdms-q1-2024%20(1).webp)

















